Skeletal System And Homeostasis
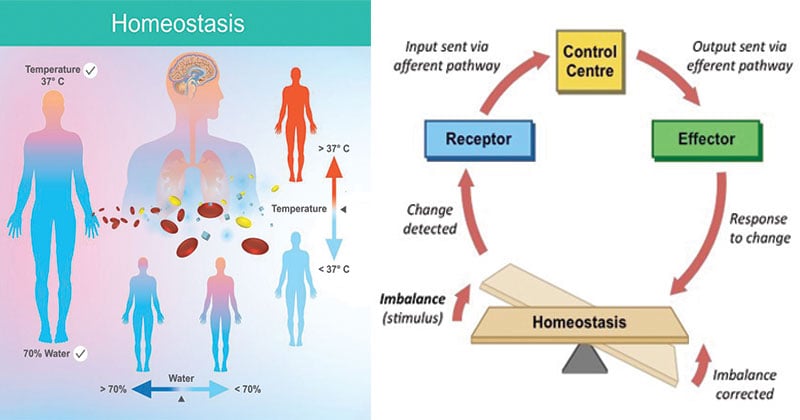
Skeletal system and homeostasis. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated having a striped appearance due to the arrangement. Homeostasis literally means same state and it refers to the process of keeping the internal body. This means that the contraction of muscle cells will lead to the shortening of muscles while the bone retains its shape.
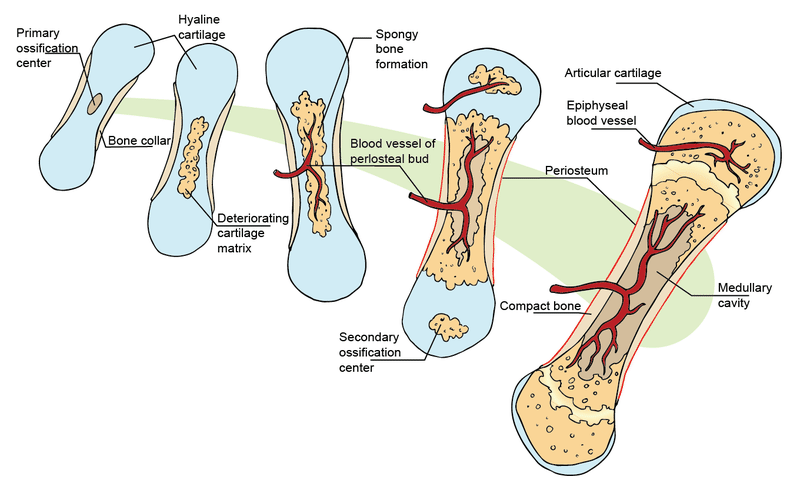
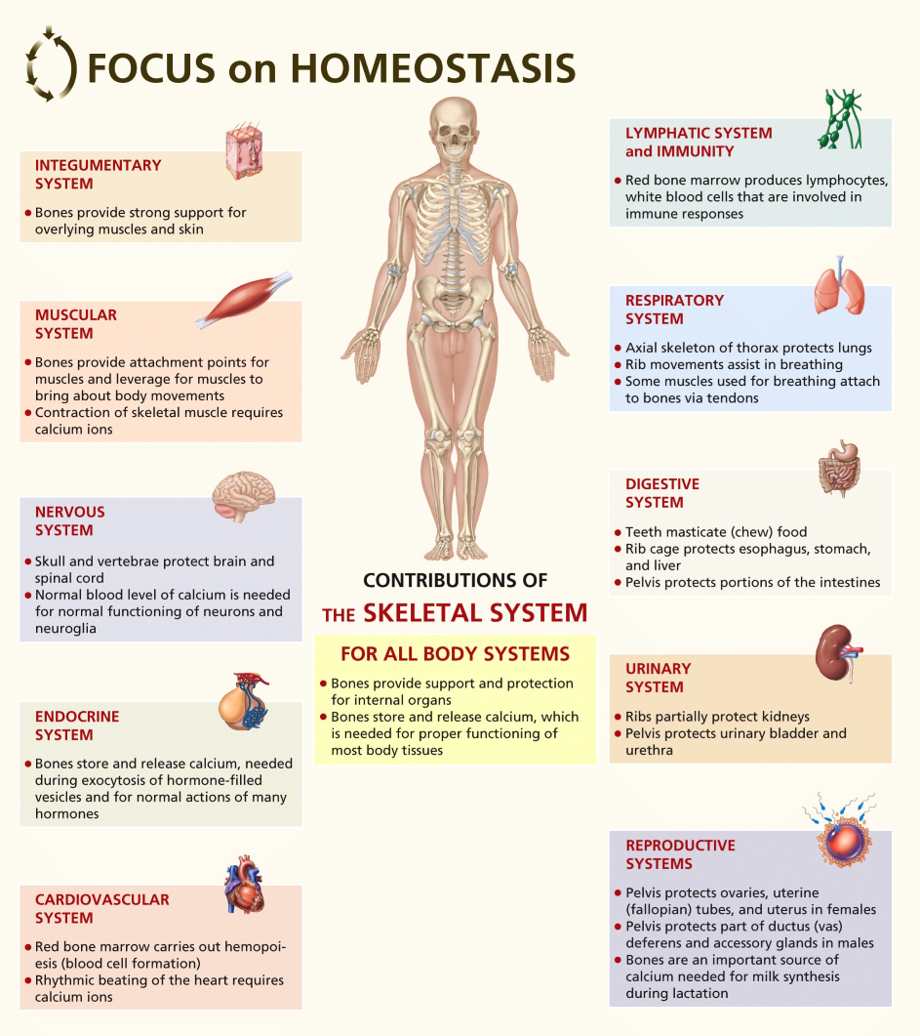
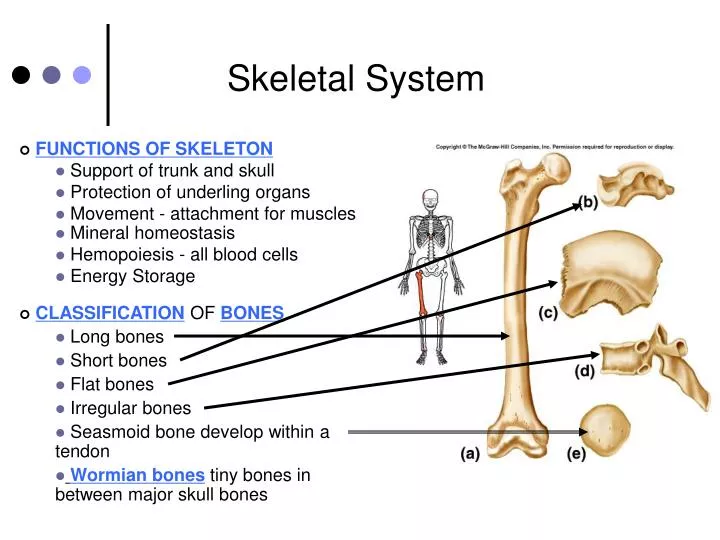
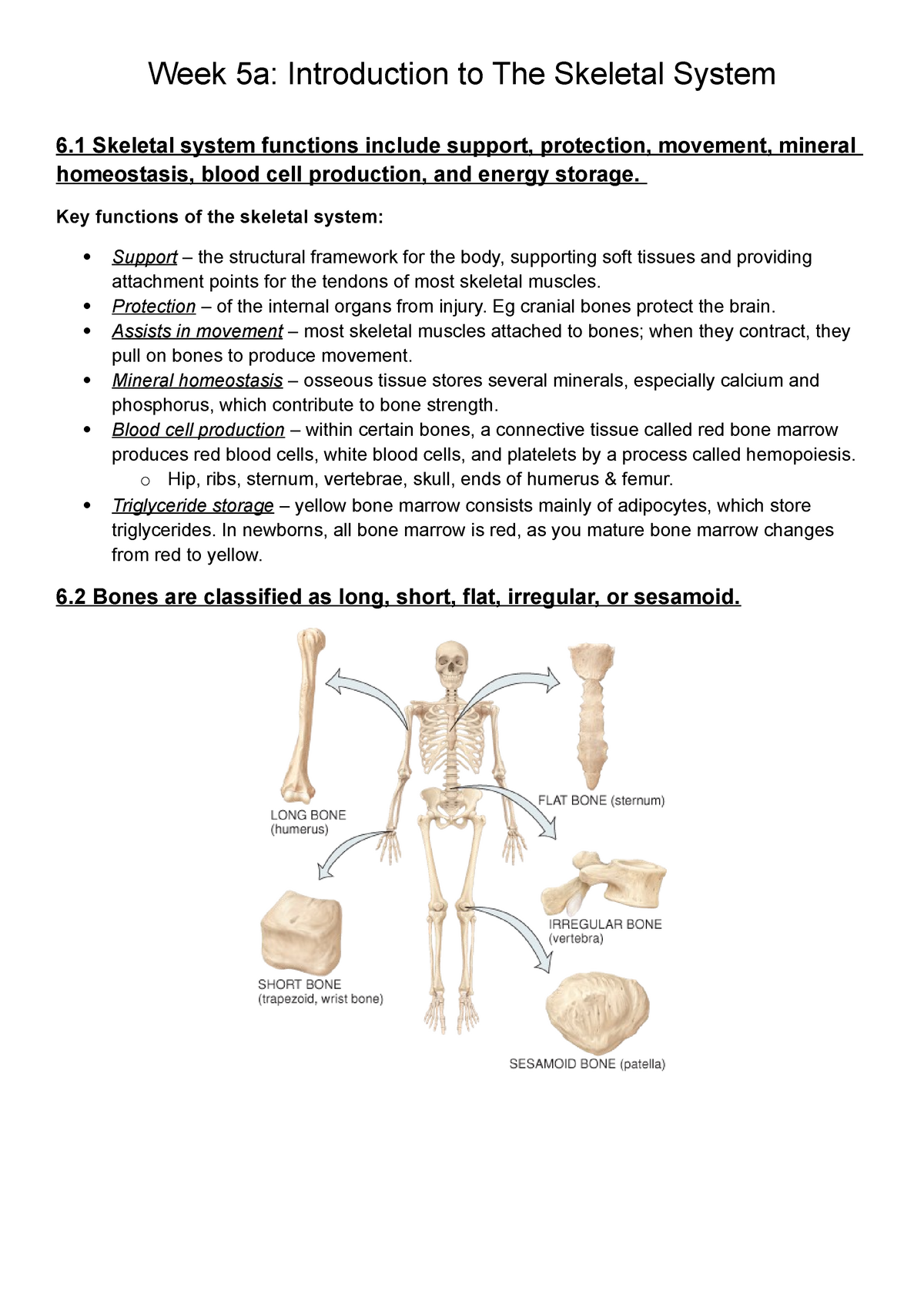
Bone tissue or osseous tissue is a hard dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton the internal support structure of the body. The skeletal system helps maintain homeostasis. This article the first in a two-part series on the structure and function of the skeletal system reviews the anatomy and physiology of bone.
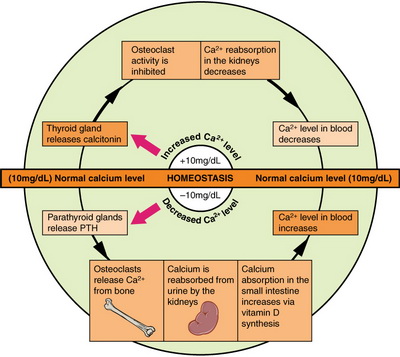
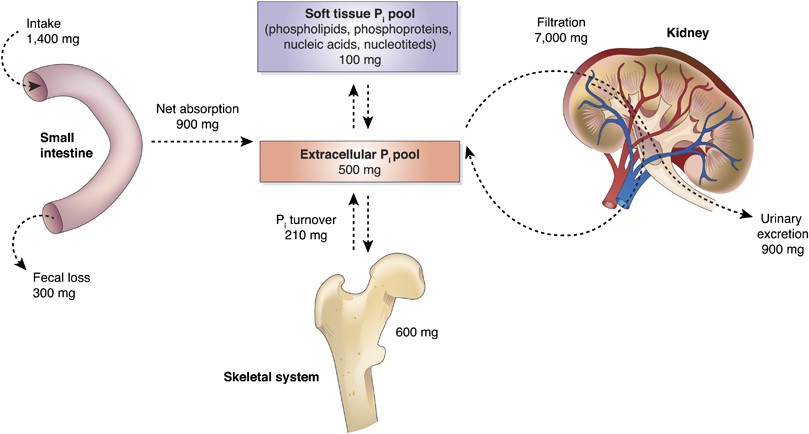
Sodium calcium and potassium must be closely regulated. Your muscles generate heat. B Physiologic example of nested homeostatic units.
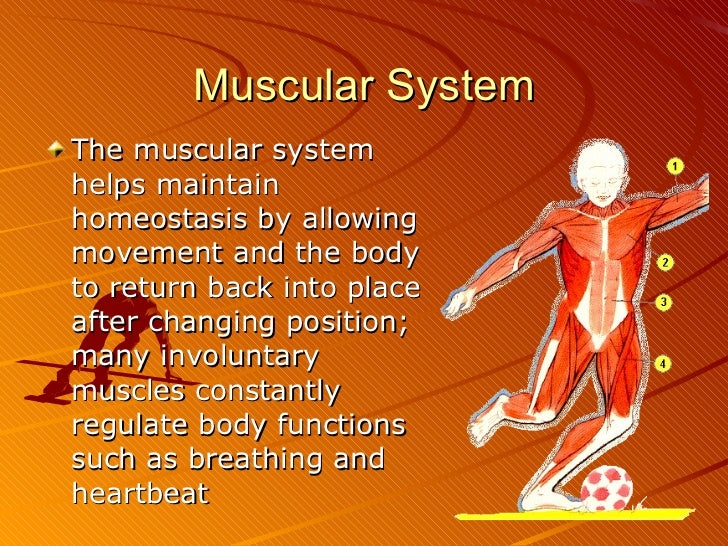
The muscular system maintains homeostasis by a number of different ways. It is the center of all mental activity including thought learning and memory. The average persons skin weighs 10 pounds and has a surface area of almost 20 square feet.
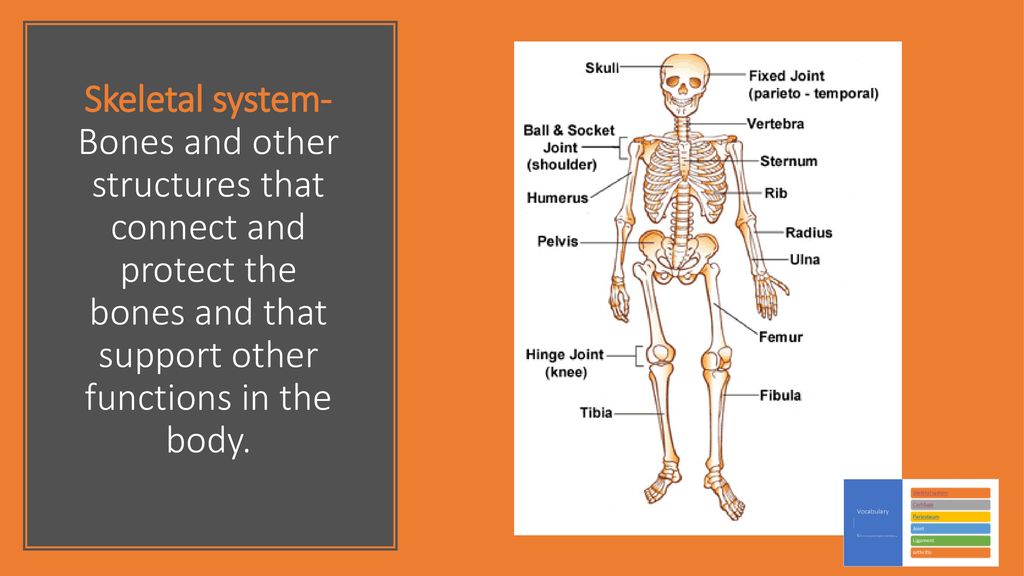
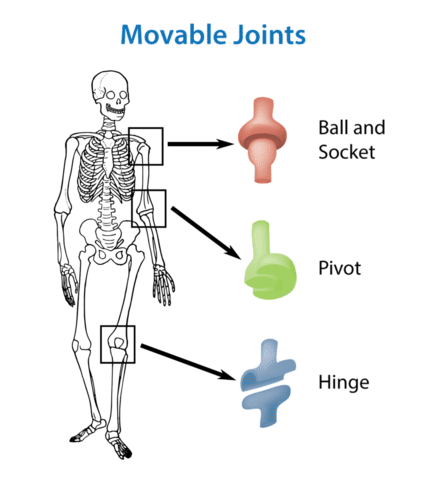
In the areas of the skeleton where whole. The skeletal system is formed of bones and cartilage which are connected by ligaments to form a framework for the remainder of the body tissues. Red cells are very important to the human body because they carry oxygen to the bodys tissue and they also carry carbon dioxide out to the lungs where it is eliminated.
This system gives your body its shape and form. Failure of K regulation can have serious consequences on nerve conduction skeletal muscle function and most significantly on cardiac muscle contraction and. In Module 2 we.
Human skeleton the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. The nervous system is the major controlling regulatory and communicating system in the body.
In the areas of the skeleton where whole.
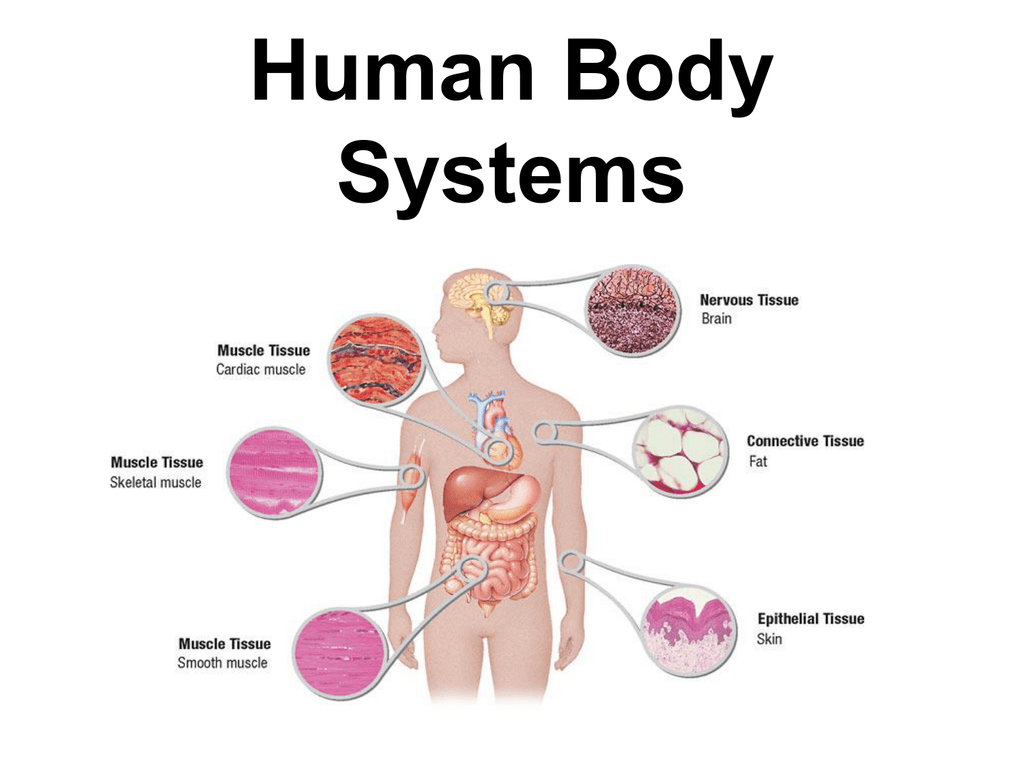
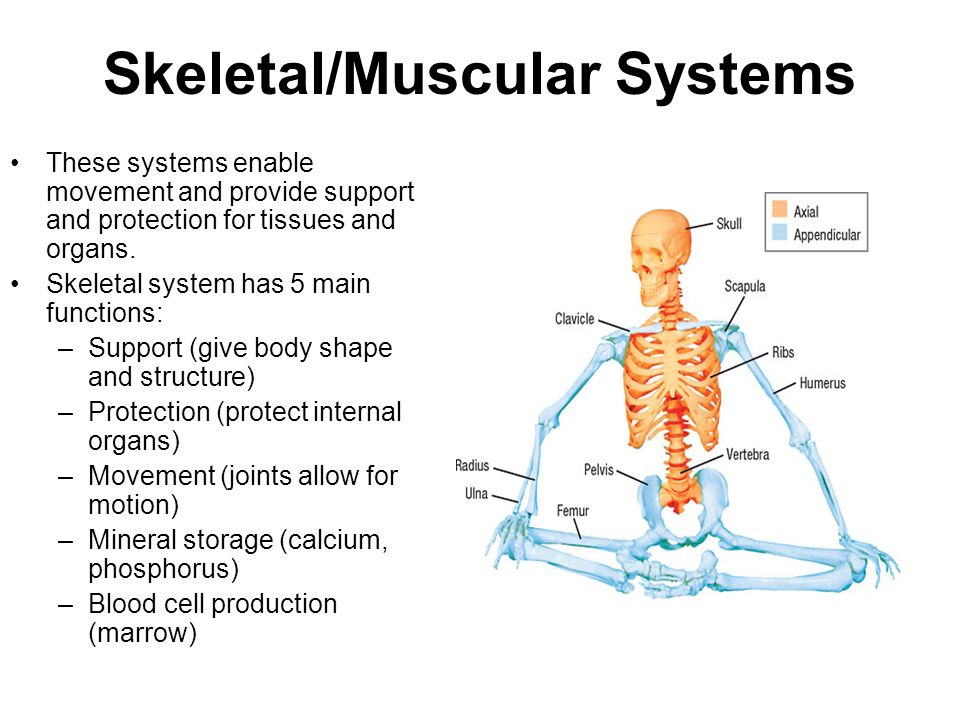
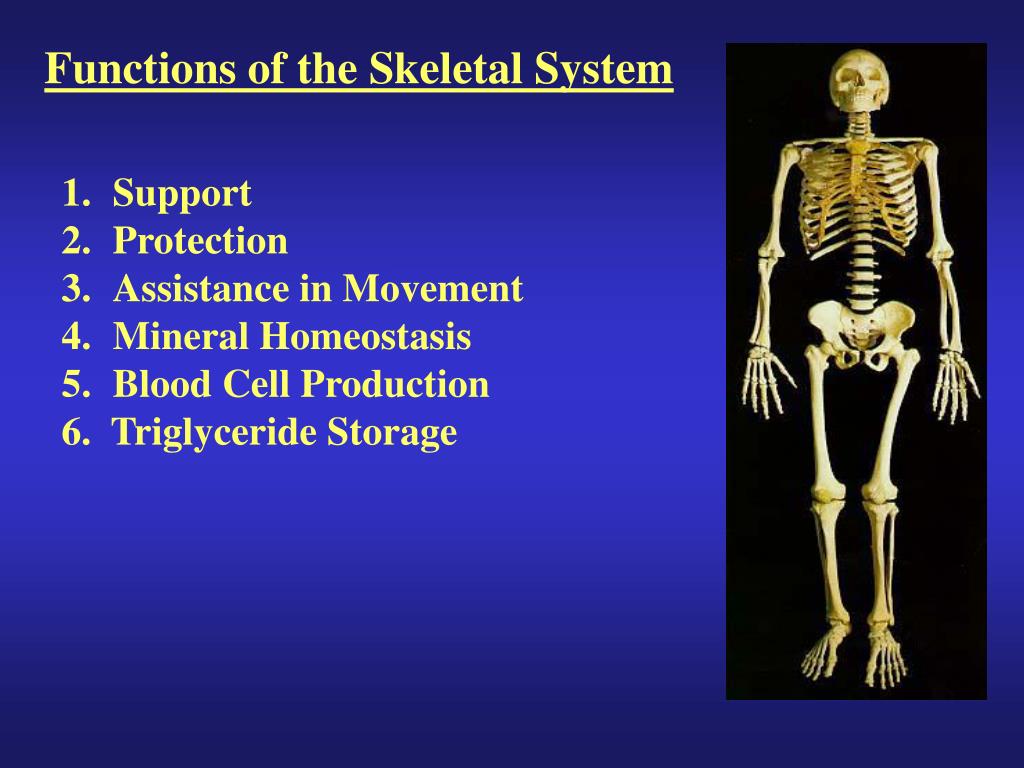
Much of the hormone system and autonomic nervous systems is dedicated to homeostasis and their action is coordinated by the hypothalamus. Skeletal muscles commonly referred to as muscles are organs of the vertebrate muscular system that are mostly attached by tendons to bones of the skeleton. The changes that are part of normal metabolism may be internal or external and the organism must respond appropriately. Rho guanosine triphosphate hydrolases GTPases are molecular switches that cycle between an inactive guanosine diphosphate GDP-bound and an active guanosine triphosphate GTP-bound state during signal transduction. Calcium is needed for muscle contraction and nerve impulse conduction. The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones cartilages ligaments and other tissues that perform essential functions for the human body. Paul Andersen describes the important features of the skeletal system. This article the first in a two-part series on the structure and function of the skeletal system reviews the anatomy and physiology of bone. The muscular system maintains homeostasis by a number of different ways.
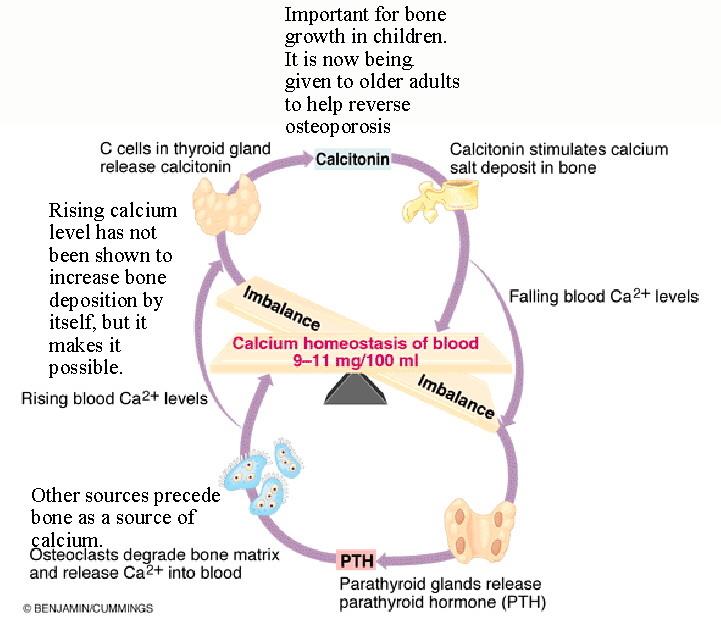
Introduction to the Nervous System. Paul Andersen describes the important features of the skeletal system. Human skeleton the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. He then explains how the human skeleton provides support movement storage blood production and homeostasis. In addition parathyroid hormone vitamin D and calcitonin also play an essential role. The amount in circulation must be kept tightly controlled inside a narrow range. Additionally these findings will describe how MyD88 signaling in skeletal cells contributes to immune defenses and affects the kinetics of bone remodeling.






















Post a Comment for "Skeletal System And Homeostasis"